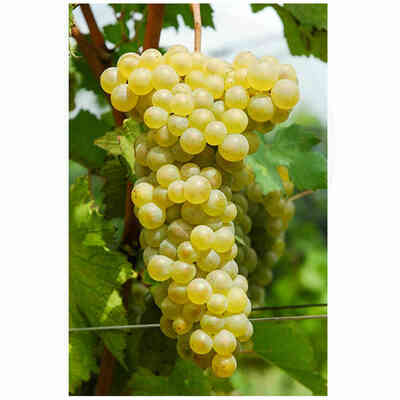
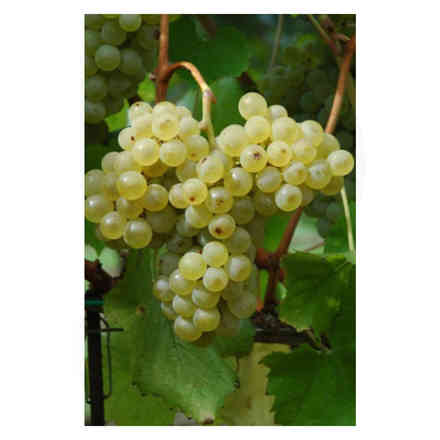
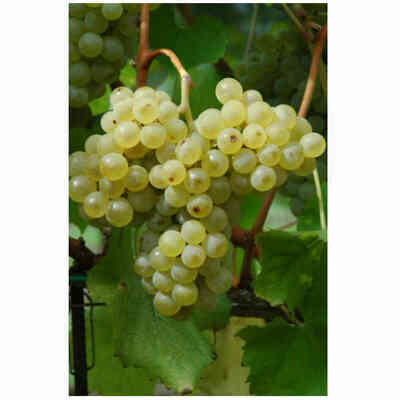
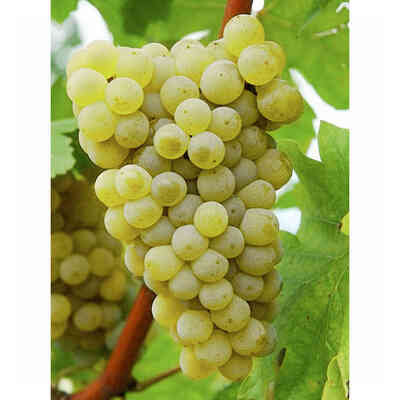
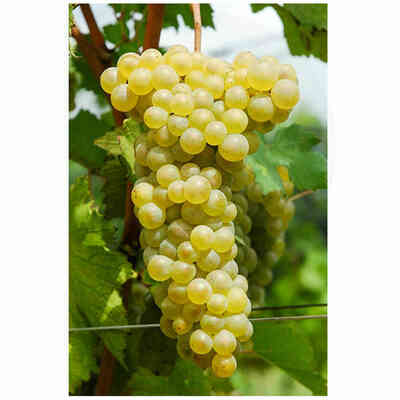
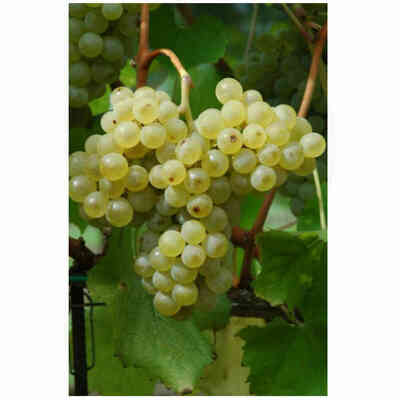
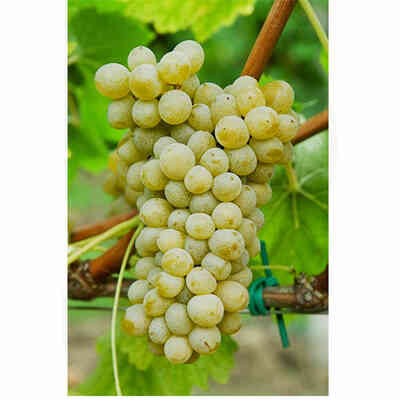
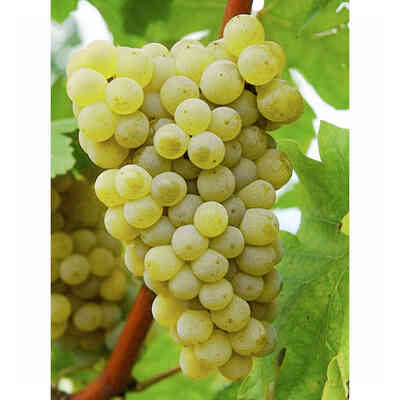
Verdicchio (10 pieces)
Description
 AUTHORIZED RETAILER
AUTHORIZED RETAILER
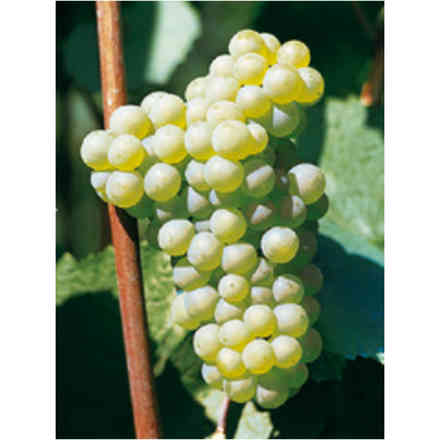
Barbatella Verdicchio (10 pieces)
Rootstocks: 1103P - K5BB - S04 - 140RU - 420A (We will send the graft carrier available at the time)
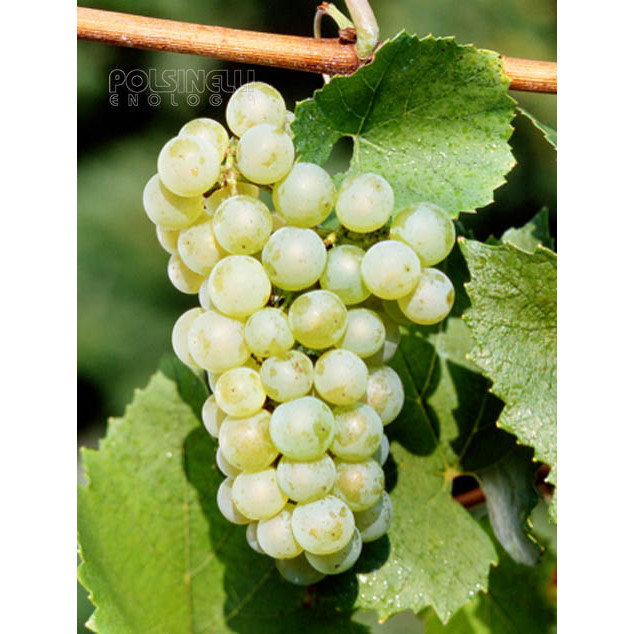
Grape variety of ancient origin, already known in Roman times, it is mainly cultivated in the Marche region and sporadically in neighbouring regions. Like Trebbiano di Soave or Lugana, it is widespread in the area of Lake Garda and in the provinces of Verona and Brescia.
- Ampelographic characteristics: the variety is relatively homogeneous; differential characteristics concern the vigour and position of the fruiting buds, the shape of the bunch and the colour of the berry. It is identical to Trebbiano di Soave. Bud with expanded apex, cottony, whitish-green with pinkish shades at the edges. The leaves are medium-sized, pentagonal, trilogate or quinquelobate, slightly wavy, dark green, with a cottony underside. Petiolar sinus in the shape of a closed lyre with margins sometimes overlapping. Cluster: medium, compact or semi-compact, conical, winged. Berry: medium, round, yellowish-green in colour; firm, slightly pruinose skin; juicy pulp with a simple, sweet flavour.
- Cultivation requirements: vigorous vine with semi-erect vegetation habit. Robust shoot with medium internodes. Prefers clayey soils and well exposed and airy hillside areas for a healthy and complete ripening of the grapes.
- Cultivation and pruning: prefers medium forms of cultivation and long pruning. It is difficult for it to adapt to forms for full mechanisation because of the delicacy of the grapes. Traditional espalier forms are recommended, with appropriate greening to avoid attacks of cryptogams on the bunches.
- Sprouting time: medium-late.
- Ripening time: medium-late.
- Production: good and relatively constant.
- Sensitivity to disease and adversity: poor resistance to cryptogams, in particular to powdery mildew and botrytis. Good resistance to late cold, less so to winter cold.
- Oenological potential: gives a straw-yellow coloured wine with greenish reflections, pleasantly bitterish, slender in body, lively, with a dry flavour and a subtle, delicate aroma. With good structure and acidity, it is also suitable for short ageing.
AREA CULTIVATED IN ITALY
YEAR 1970 1982 1990 2000 2010
HECTARES 3,863 3,831 3,919 3,714 2,300
RULES TO PLANT A VINEYARD
1. PLOW
You must perform this operation always with dry soil
A) On arable land is generally sufficient to ripper + to plow
B) On planting soil is generally sufficient to plow with an escavator and to clean the old roots.
If the previous crop was a vineyard, it is a good idea to leave the soil fallow for at least three years (after plowing). This procedure represents a valid possibility of defence against soil nematodes.
2. SOIL FERTILIZATION
Use organics and if it is a reimplantation, use Calciumocyanamide.
This fertiliser has a protective effect on the soil and the crop, especially against fungi.
3.PROPAGATING GRAPE VINE CUTTINGS
The planting should be carried out in temperate soil. The grafting point should be 8-10 cm above ground. Avoid shaving the redices. As much as possible, put sand and/or peat in contact with the roots (the root fears asphyxiation, while it needs a micro-oxygenation). Never fertilize in a localized manner (near the roots). Never water the rooted cuttings before summer.
4.SPRING WORKS
When sprouting, the root apparatus must be heated as soon as possible. Work the soil repeatedly every 7/10 days at increasing depth (up to 20 cm), taking into account the moisture of the soil. When the apex of the bud starts to grow, it means that the root system is functioning. Only then can we stop watering the soil. Failure to grow due to access to water is often confused with a lack of water. This is why watering is used which is expensive, useless or even worse.
5.SPRING CURE
Protect vegetation from Peronospora. To each treatment add nitrogen (N) and iron (Fe) foliar fertilizer. Do not make any radical fertilization.
6.SUMMER CURE
Continue with the defense against Peronospora by suspending the addition of the foliar fertilizer. This defense should be reinforced in late summer and should be continued until vegetation growth stops.
The September/October blight is destructive, to the point of bringing death to the whole plant (if it has not lignified). The rooted vine lacks clusters, so lignification occurs at the end of the vegetative cycle.
7.TECHNICAL VISIT
If incomprehensible anomalies persist after this procedure, contact an agronomist or the VCR Technical Service promptly before carrying out arbitrary procedures which may be unsuitable, expensive and/or worsening.